## Introduction
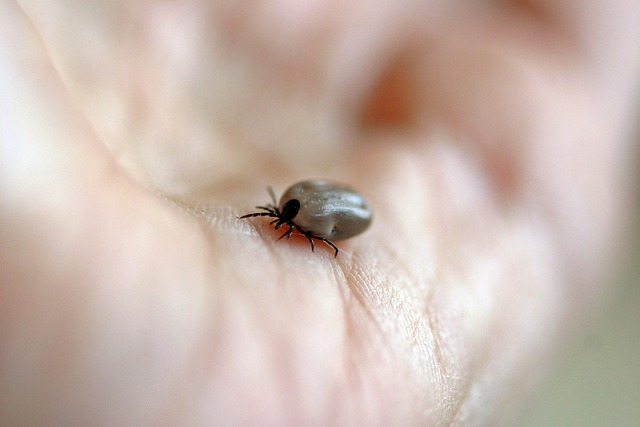
Scrub typhus is a re-emerging infectious disease that poses a significant threat to public health in India. Caused by the bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi, scrub typhus is transmitted to humans through the bite of chiggers, which are mite larvae of the Trombiculidae family. The disease manifests with symptoms such as fever, headache, nausea/vomiting, and breathlessness, and if left untreated, it can lead to life-threatening complications. In recent years, there has been a surge in the number of scrub typhus cases reported in India, highlighting the need for increased awareness and effective control measures.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Scrub typhus is geographically restricted to the Asia Pacific region, with an estimated one billion people at risk. India, in particular, has been significantly affected by the disease, with almost a million cases reported each year. The disease primarily affects individuals engaged in agricultural activities, such as farmers and agricultural workers, as well as housewives who are exposed to the vector in rural areas. Factors contributing to the increased risk of scrub typhus include changes in land use and urbanization, population growth, and climate change.
Clinical Presentation and Complications
The clinical presentation of scrub typhus can vary, but common symptoms include fever, headache, breathlessness, and nausea/vomiting. One of the characteristic features of scrub typhus is the presence of an eschar, a painless ulcer at the site of the chigger bite. Complications associated with scrub typhus can be severe and life-threatening. These include acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), hypotension requiring ionotropic support, hepatitis, meningoencephalitis, and renal impairment. Prompt recognition and early treatment are crucial in preventing the progression of the disease and reducing the risk of complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing scrub typhus can be challenging due to its nonspecific clinical presentation and the lack of awareness among healthcare professionals. Laboratory testing, including serological assays such as IgM ELISA, is commonly used to confirm the diagnosis. Molecular techniques such as PCR and sequence analysis can further confirm the presence of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Early initiation of appropriate antibiotic therapy, primarily with doxycycline, is essential in the management of scrub typhus. In most cases, patients show a dramatic response to doxycycline, with fever defervescence occurring within a few days of treatment.
Factors Contributing to the Re-emergence of Scrub Typhus
The re-emergence of scrub typhus in India can be attributed to various factors. Changes in land use and urbanization have resulted in the encroachment of human settlements into previously undisturbed areas, increasing the risk of exposure to chigger-infested environments. Population growth has led to overcrowding and inadequate sanitation, creating favorable conditions for the transmission of the disease. Climate change, including rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns, may also play a role in the proliferation of chigger populations. Additionally, the availability of better diagnostic tests and increased awareness among healthcare professionals have contributed to the detection and reporting of more cases.
Prevention and Control Strategies
Preventing scrub typhus requires a comprehensive approach that includes vector control, health education, and early diagnosis and treatment. Vector control measures, such as the use of insect repellents, protective clothing, and environmental management, can help reduce exposure to chiggers. Public awareness campaigns aimed at promoting personal hygiene, proper sanitation practices, and the recognition of symptoms can facilitate early diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare professionals should be trained to recognize and manage scrub typhus cases effectively. Additionally, research efforts should focus on the development of effective vaccines to prevent scrub typhus.
Surveillance and Reporting
Accurate surveillance and reporting of scrub typhus cases are crucial for monitoring disease trends, identifying high-risk areas, and implementing targeted control measures. Standardized surveillance systems should be implemented at both the national and regional levels to ensure timely and accurate data collection. Healthcare facilities and laboratories should report confirmed scrub typhus cases to the relevant authorities, enabling a better understanding of the disease burden and facilitating appropriate public health interventions.
Conclusion
Scrub typhus poses a growing threat to public health in India, with a significant number of cases reported each year. The re-emergence of the disease can be attributed to various factors, including changes in land use, urbanization, population growth, and climate change. Early diagnosis, prompt treatment with doxycycline, and effective control measures, such as vector control and public awareness campaigns, are essential in mitigating the impact of scrub typhus. Continued research and surveillance efforts are needed to gain a better understanding of the disease and develop strategies for its prevention and control.