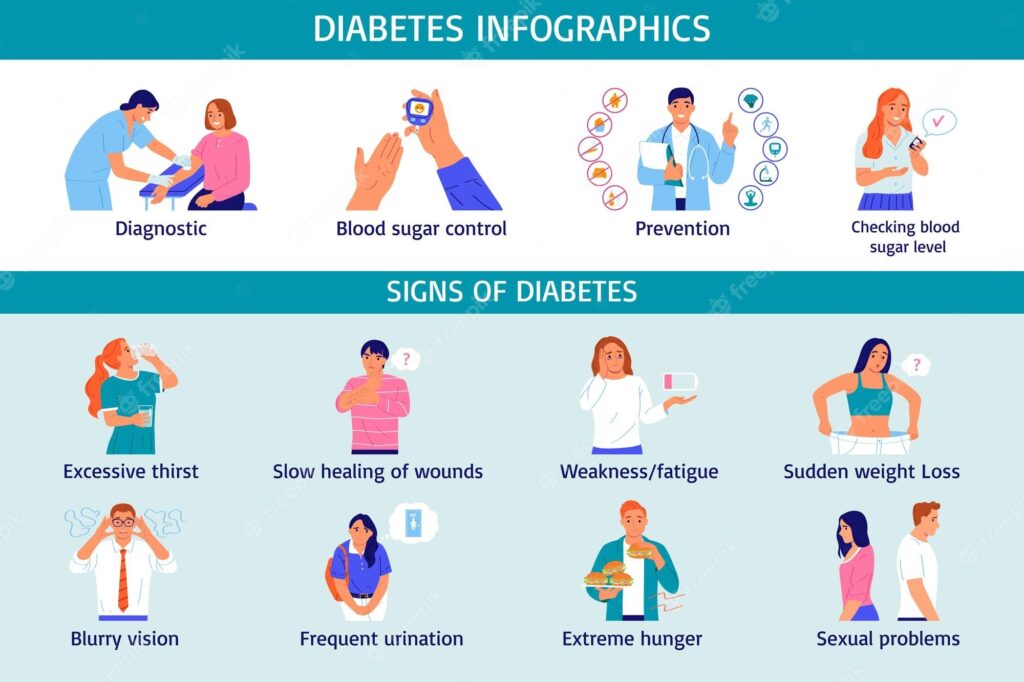
Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires careful management of blood sugar levels. By following specific dietary guidelines, individuals with diabetes can effectively control their condition and prevent blood sugar spikes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the do’s and don’ts of managing blood sugar levels, providing you with practical tips and insights to help you maintain optimal health.
1. Embrace Whole Grains and Limit Refined Carbs
Starchy foods are an essential part of a balanced diet, providing the body with necessary energy. However, it’s crucial to make mindful choices when it comes to carbohydrates, opting for whole grains instead of refined carbs. Whole grain products, such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, and oats, contain more fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to their refined counterparts. These nutrients help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of sudden spikes. On the other hand, foods like white bread, white rice, deep-fried items, and Indian sweets like laddoos and halwas should be avoided, as they can quickly elevate blood sugar levels.
Do:
- Choose whole wheat bread, brown rice, and oats for a healthier carbohydrate option.
- Opt for whole grain products that provide more nutrients and fiber.
- Incorporate whole grains into your diet to prevent rapid blood sugar spikes.
Don’t:
- Consume white bread, white rice, deep-fried foods, and sugary Indian sweets.
- Rely on refined carbohydrates that can lead to sudden increases in blood sugar levels.
2. Enjoy a Variety of Fruits in Moderation
Fruits are a natural source of carbohydrates and offer an array of essential nutrients. While fruits are generally healthy, they can still affect blood sugar levels due to their natural sugar content. It’s important to consume fruits in moderation and pay attention to portion sizes. Choose fruits with a lower glycemic index, such as apples, bananas, and oranges, as they cause a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Avoid processed fruits like canned fruits and fruit juices, as they often contain added sugars that can quickly raise blood sugar levels.
Do:
- Include small portions of fruits like apples, bananas, and oranges in your diet.
- Opt for whole fruits instead of processed options, as they have a lower impact on blood sugar levels.
Don’t:
- Overindulge in fruits, as excessive consumption can lead to higher blood sugar levels.
- Consume canned fruits or fruit juices that may contain added sugars.
3. Prioritize Nutrient-Dense Vegetables
Vegetables are a vital component of a balanced diet for individuals with diabetes. They are low in calories, rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, and have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Incorporating a variety of vegetables into your meals can help regulate blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients for overall health. Opt for vegetables such as spinach, tomatoes, green beans, cucumbers, broccoli, cauliflower, and sweet potatoes, as they are packed with nutrients and low in carbohydrates. Avoid fried and breaded vegetables, as they can add unnecessary calories, carbs, and fat to your diet.
Do:
- Include a variety of vegetables, such as spinach, tomatoes, and broccoli, in your daily meals.
- Opt for steamed or tawa-fried vegetables instead of deep-fried options.
- Enjoy vegetables that provide essential nutrients and are low in carbohydrates.
Don’t:
- Consume fried and breaded vegetables, as they contain excess calories, carbs, and fat.
- Overlook the importance of nutrient-dense vegetables in your diet.
4. Choose Lean Sources of Protein
Protein is an essential macronutrient that helps stabilize blood sugar levels and promotes satiety. When selecting sources of protein, opt for lean options to avoid excessive fat intake. Skinless chicken, fish, rajma (kidney beans), moong (mung beans), soya beans, and lean cuts of meat are excellent choices. Including plant-based protein sources such as beans, nuts, or tofu can provide additional fiber and nutrients that animal-based proteins may lack.
Do:
- Choose lean sources of protein such as skinless chicken, fish, and legumes.
- Include plant-based proteins like beans, nuts, and tofu for added fiber and nutrients.
Don’t:
- Consume fatty cuts of meat or processed meat products.
- Overlook the importance of lean protein sources in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
5. Be Mindful of Dairy Consumption
Milk and dairy products can be part of a healthy diet for individuals with diabetes. However, it’s essential to make wise choices to avoid excessive calorie and saturated fat intake. Opt for unflavored, low-fat dairy products like yogurt, milk, and paneer (cottage cheese) to obtain protein, calcium, vitamins, and minerals without the added fat. Full-fat dairy products should be avoided, as they contribute to plaque buildup and increase the risk of heart disease, which is already heightened in individuals with diabetes.
Do:
- Choose unflavored, low-fat dairy products like yogurt, milk, and paneer for their nutritional benefits.
- Enjoy dairy products that provide protein, calcium, and vitamins without excessive fat content.
Don’t:
- Consume full-fat dairy products that can contribute to increased cholesterol levels and heart disease risk.
6. Emphasize Healthy Fats and Oils
While it’s important to limit overall fat intake, not all fats are harmful. Opt for healthier fats and oils, such as sesame seed oil, olive oil, and mustard oil, which provide essential fatty acids and promote heart health. Additionally, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet through foods like tuna fish and mackerel can have additional cardiovascular benefits. Avoid saturated and partially hydrogenated fats found in animal products and certain plant oils, as they can negatively impact blood sugar control and increase the risk of heart disease.
Do:
- Choose healthier fats and oils like sesame seed oil, olive oil, and mustard oil.
- Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as tuna fish and mackerel, to promote heart health.
Don’t:
- Consume saturated and partially hydrogenated fats found in animal products and certain plant oils.
- Overlook the importance of incorporating healthy fats into your diet.
7. Stay Hydrated with Water
Water plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and regulating blood sugar levels. It is a neutral beverage that neither raises nor lowers blood sugar. Staying hydrated helps dilute your blood, preventing dehydration and potential blood sugar imbalances. The Mayo Clinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/water/art-20044256 recommends men aim for approximately 15½ cups of fluid per day, while women should target around 11½ cups. Carry a water bottle with you to ensure you have access to water throughout the day, and monitor your hydration by checking the color of your urine, aiming for a light yellow color.
Do:
- Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
- Carry a water bottle with you to ensure you have access to water at all times.
Don’t:
- Neglect staying hydrated, as it can lead to dehydration and potential blood sugar imbalances.
8. Be Mindful of Portion Sizes
Portion control is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy weight. Even healthy foods can impact blood sugar levels if consumed in large quantities. Be mindful of portion sizes and aim for balanced meals that include a variety of food groups. Consulting a registered dietitian can provide valuable guidance on appropriate portion sizes and meal planning specific to your needs.
Do:
- Practice portion control to prevent excessive calorie and carbohydrate intake.
- Seek guidance from a registered dietitian for personalized portion size recommendations.
Don’t:
- Overindulge in any food, even if it is considered healthy.
- Neglect portion control, as it plays a vital role in blood sugar management.
9. Regularly Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an essential part of diabetes management. Regularly checking your blood sugar levels helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood glucose levels. It allows you to make informed choices and adjust your diet and medications accordingly. Carry a glucometer with you to conveniently check your blood sugar levels at the right time and respond promptly to any fluctuations.
Do:
- Keep a glucometer with you to regularly monitor your blood sugar levels.
- Use the results to make informed decisions about your diet, medication, and overall diabetes management.
Don’t:
- Neglect monitoring your blood sugar levels, as it is crucial for successful diabetes management.
10. Seek Professional Guidance
Managing diabetes is a complex process that requires individualized care. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare team, including your physician, registered dietitian, and diabetes educator. They can provide personalized dietary recommendations, assist in creating meal plans, and offer support and guidance throughout your diabetes journey. Regular check-ups and communication with your healthcare team will ensure you stay on track and effectively manage your blood sugar levels.
Do:
- Collaborate with healthcare professionals, including your physician, registered dietitian, and diabetes educator.
- Seek personalized guidance and support for your diabetes management.
Don’t:
- Attempt to manage diabetes on your own without professional guidance.
- Neglect regular check-ups and communication with your healthcare team.
By following these do’s and don’ts, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and maintain optimal health. Remember, diabetes management is a lifelong commitment, and small lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in your overall well-being. Stay informed, make mindful choices, and prioritize your health to live a fulfilling life with diabetes.