Introduction to the Nipah Virus
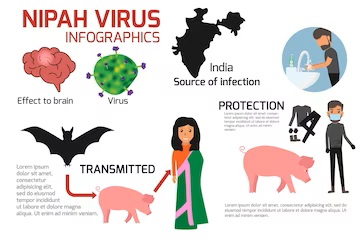
The Nipah virus is a newly emerging zoonotic virus that was first identified in the year 1999 during an outbreak in Malaysia. This highly contagious virus belongs to the RNA virus family and is known to cause severe illness and even death in humans. Nipah virus is primarily transmitted to humans from animals, specifically fruit bats or through direct contact with infected pigs. Since its discovery, Nipah virus has caused several outbreaks in different parts of the world, including India. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms of this new virus and discuss the measures to prevent its spread.
Understanding RNA Viruses and Nipah
RNA viruses, such as the Nipah virus, are a group of viruses that have RNA as their genetic material instead of DNA. These viruses are known for their ability to mutate rapidly, making it difficult to develop effective treatments or vaccines. The Nipah virus, specifically, belongs to the Henipavirus genus within the Paramyxoviridae family. It is a negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus, which means that it carries its genetic information in the form of RNA that is complementary to the viral genome. This unique characteristic of RNA viruses allows them to hijack the host’s cellular machinery and replicate rapidly, leading to the manifestation of various symptoms.
History and Outbreaks of Nipah Virus
The first recognized outbreak of Nipah virus occurred in Malaysia in 1999, where it caused severe respiratory illness and encephalitis in humans. The transmission of the virus was traced back to contact with infected pigs, which acted as intermediate hosts between fruit bats and humans. Since then, Nipah virus outbreaks have been reported in different parts of the world, including Bangladesh, India, and even Singapore. The mortality rate of Nipah virus infection can be as high as 75%, making it a significant public health concern. The recurrent outbreaks highlight the need for continuous surveillance and research to understand the virus better and develop effective prevention and control strategies.
Symptoms of Nipah Virus
The symptoms of Nipah virus infection can vary from mild to severe, depending on the individual’s immune response and the viral load. The incubation period of the virus ranges from 4 to 14 days, during which infected individuals may not exhibit any symptoms. However, once the symptoms manifest, they can include fever, headache, dizziness, sore throat, and muscle pain. As the infection progresses, more severe symptoms such as respiratory distress, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), seizures, and even coma can occur. It is crucial to note that Nipah virus infection can be fatal, especially in individuals with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions.
Diagnosing Nipah Virus
Diagnosing Nipah virus infection can be challenging due to its similarity to other respiratory illnesses and the need for specialized laboratory tests. In suspected cases, healthcare professionals collect samples from the respiratory tract, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid for laboratory analysis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests are commonly used to detect the presence of the virus’s genetic material in these samples. Serological tests, which detect the antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the virus, can also be employed. Timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and containment of the virus.
Treatment Options for Nipah Virus – Ribavirin and NIV
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment available for Nipah virus infection. Supportive care and management of symptoms are the mainstay of treatment. However, some experimental treatments have shown potential in limited studies. Ribavirin, an antiviral medication commonly used for other viral infections, has been tested in some cases of Nipah virus infection. While its effectiveness is still under investigation, early administration of ribavirin has shown promising results in some patients. Another potential treatment option is the use of the Nipah Immune Globulin (NIV), which contains antibodies against the virus. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate the efficacy of these treatments and to explore other therapeutic approaches.
Preventing the Spread of Nipah Virus
Preventing the spread of Nipah virus requires a multi-pronged approach involving public health measures, surveillance, and community awareness. Strict infection control practices, such as proper hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment, and isolation of infected individuals, are crucial in healthcare settings. Educating the public about the risks associated with Nipah virus and promoting preventive measures, such as avoiding contact with sick animals and refraining from consuming raw date palm sap, can help reduce the transmission of the virus. Additionally, active surveillance of animal populations, especially pigs and bats, can aid in early detection and containment of potential outbreaks.
Current Nipah Virus Outbreaks in India
India has been grappling with recurrent Nipah virus outbreaks in recent years. The most recent outbreak occurred in 2021 in the state of Kerala, resulting in several deaths and causing widespread panic. The Indian government, along with international organizations, promptly initiated response measures, including contact tracing, quarantine, and public awareness campaigns. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, researchers, and policymakers are crucial in addressing the challenges posed by the virus and preventing further outbreaks. Continuous monitoring and surveillance of potential hotspots can help identify and contain the virus before it spreads to larger populations.
Latest News and Updates on Nipah Virus
Staying informed about the latest news and updates on Nipah virus is essential in understanding the evolving nature of the virus and the preventive measures to be taken. Regularly monitoring reputable sources, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and World Health Organization (WHO), can provide reliable information on the current status of the virus, ongoing research, and guidelines for prevention and management. It is important to rely on accurate information from trusted sources to avoid misinformation and unnecessary panic.
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Prepared for New Viruses
As we navigate through the challenges posed by new viruses like Nipah, staying informed and prepared is of utmost importance. The emergence of Nipah virus and its recurrent outbreaks remind us of the need for robust surveillance systems, research, and collaboration between nations to effectively respond to such threats. By understanding the symptoms, transmission routes, and preventive measures associated with Nipah virus, we can contribute to the collective efforts in preventing its spread and protecting public health. Regularly updating ourselves with the latest information and guidelines from trusted sources ensures that we are well-prepared to face the challenges of new viruses like Nipah.
Click here for more information on Nipah virus from the CDC.