## Introduction to Hypertension Guidelines
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent complications. Staying updated with the latest hypertension guidelines is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. These guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of hypertension. By understanding and following these guidelines, we can effectively control blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
The Importance of Staying Updated with Hypertension Guidelines
Medical research and advancements continually shape our understanding of hypertension. As a result, guidelines are periodically updated to reflect the latest evidence-based practices. Staying informed about these updates is essential as it ensures that healthcare providers deliver the best possible care to their patients. For individuals, being aware of the latest guidelines empowers them to actively participate in their own healthcare and make informed decisions regarding lifestyle modifications, medications, and monitoring their blood pressure.
Key Changes in the Latest Hypertension Guidelines
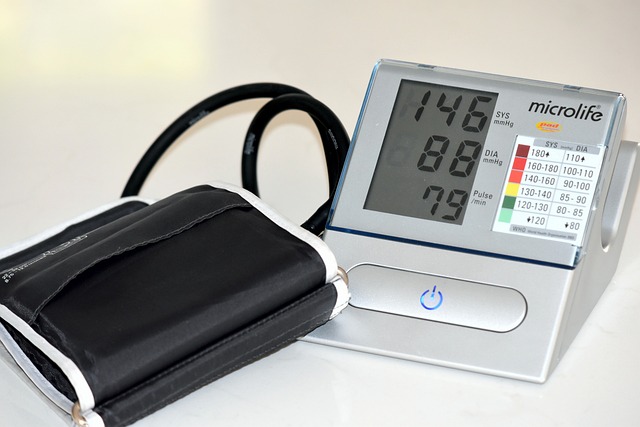
The latest hypertension guidelines have introduced significant changes that impact the diagnosis and management of the condition. One notable change is the redefinition of hypertension thresholds. Previously, a blood pressure reading of 140/90 mmHg or higher indicated hypertension. However, the latest guidelines have lowered the threshold to 130/80 mmHg, considering the increased risk of cardiovascular diseases even at slightly elevated blood pressure levels. This change means that more individuals fall within the hypertensive range, emphasizing the need for early intervention and lifestyle modifications.
Understanding Diastolic Blood Pressure and Its Impact on Hypertension
Diastolic blood pressure is the lower number in a blood pressure reading and represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. It is an essential component in the diagnosis and management of hypertension. High diastolic blood pressure can indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Understanding the role of diastolic blood pressure in hypertension is crucial as it helps healthcare professionals assess the severity of the condition and determine appropriate treatment strategies.
Risk Factors for High Diastolic Blood Pressure
Several factors contribute to high diastolic blood pressure. One significant risk factor is age. As we get older, the arteries tend to become narrower and less flexible, leading to increased resistance and higher blood pressure. Other risk factors include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, excessive salt intake, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and kidney disease. By identifying and addressing these risk factors, individuals can effectively manage their diastolic blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications.
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing High Diastolic Blood Pressure
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing high diastolic blood pressure. Adopting a healthy diet, such as the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, can significantly lower blood pressure. This diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products while limiting sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and strength training, can also improve blood pressure levels. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress-related hypertension.
Medications Recommended for Treating High Diastolic Blood Pressure
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to manage high diastolic blood pressure. Medications can be prescribed to lower blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of complications. Commonly prescribed medications for hypertension include angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers, diuretics, and beta-blockers. The choice of medication depends on various factors, including the individual’s overall health, medical history, and potential side effects. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate the individual’s specific needs and provide personalized treatment recommendations.
Monitoring and Tracking Your Blood Pressure Levels
Regular monitoring and tracking of blood pressure levels are crucial for individuals with high diastolic blood pressure. This can be done at home using a home blood pressure monitor or by visiting a healthcare professional regularly. By consistently monitoring blood pressure, individuals can identify any fluctuations or trends and take appropriate actions to manage their condition effectively. It is recommended to keep a record of blood pressure readings and share them with healthcare providers during check-ups to facilitate accurate diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional for Personalized Hypertension Management
While lifestyle modifications and self-monitoring are essential, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized hypertension management. Healthcare providers have the knowledge and expertise to assess an individual’s overall health, consider their medical history, and recommend appropriate treatment strategies. They can also monitor the effectiveness of medications, adjust dosages if necessary, and provide guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for optimal hypertension management.
Conclusion and the Significance of Following Hypertension Guidelines
In conclusion, understanding and following the latest hypertension guidelines are vital for effective management of the condition. These guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations that healthcare professionals and individuals can rely on to control blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. By staying updated, individuals can actively participate in their own healthcare and make informed decisions regarding lifestyle modifications and medications. Regular monitoring, consultation with healthcare professionals, and adherence to guidelines are key to successfully managing hypertension and maintaining overall health and well-being.